Table of Contents
Key takeaways:
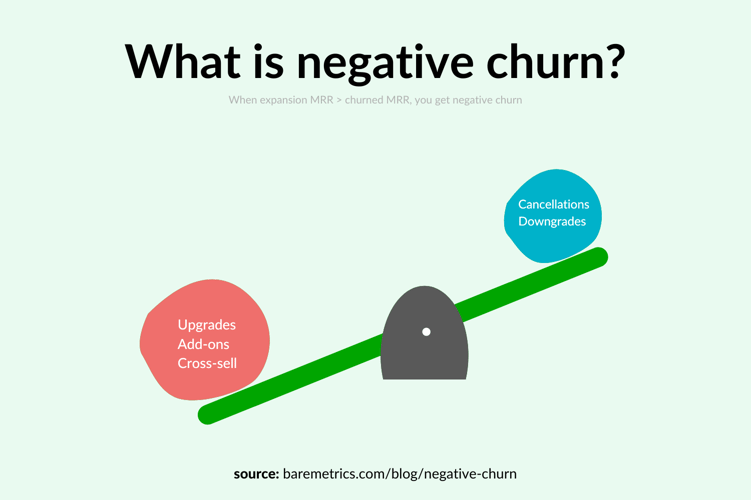
- Negative churn occurs when you retain more revenue than you lose in a set period of time, and while it’s difficult to achieve, it’s a goal many SaaS businesses share
- You can boost revenue and achieve negative churn by implementing dedicated tactics like increasing cross-sells, upsells, and identifying users at risk for churn
- You can leverage tools like Baremetrics’ Cancellation Insights or Recover to understand why users cancel, make proactive changes, and retain customers longer by reducing churn
Generally speaking, you don’t want your SaaS metrics to be negative.
Negative daily active users? Bad.
Negative revenue? Horrible.
Negative net revenue churn? Amazing!
Net revenue churn is the exception to the rule, and it’s one of the few times you’ll hear founders get excited about a KPI being in the negative.
So, why does everyone have such a positive attitude about negative churn?
Read on to find out:
- The difference between customer churn and revenue churn
- Expanding revenue with net negative churn
- Calculating negative churn
- Tracking negative churn
- Achieving negative churn
The Difference Between Customer Churn and Revenue Churn
Let’s set the stage with a couple of quick definitions.
It’s important to understand the difference between customer churn and revenue churn. Here are the basics:
- Customer churn: How many customers you’re losing each month from cancellations or involuntary churn (i.e. failed charges)
- Revenue churn: How much monthly recurring revenue (MRR) you lose each month from cancellations, involuntary churn and contraction MRR (i.e. downgrades)
When we talk about negative churn, we’re specifically talking about revenue churn (aka MRR churn)
It’s important to differentiate between the two because negative customer churn isn’t really a thing.
Now that we have that out of the way, let’s dive in!
Expanding Revenue with Net Negative Churn
Negative churn occurs when the incremental revenue generated from your existing customer base exceeds the revenue lost to cancellations and account downgrades.
Even with a high-performing product, some degree of revenue churn is inevitable as customer needs shift over time. Targeted expansion efforts—such as upgrades and cross-sells—can effectively offset churn and drive sustainable net revenue growth.
.
When SaaS businesses consider churn, the focus is often on “how do we keep as many customers and as much revenue as possible?”
Net negative revenue churn forces you to also think about how you can expand the revenue you get from your current customers which shifts you from a scarcity mindset to an abundance mindset.
Calculating Negative Churn
To calculate net negative revenue churn, you use the net revenue churn formula:
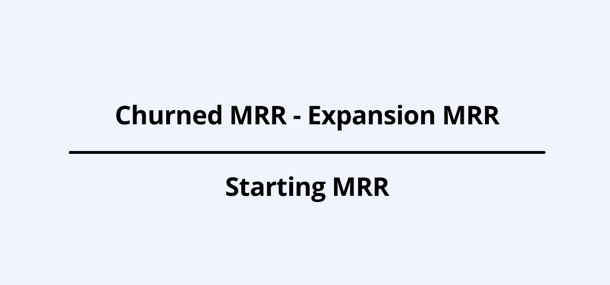
If your expansion MRR is greater than your churned MRR, you’ll get a negative number, which means you gained more revenue from existing customers than you lost.
Here’s an example.
Let’s say your company has 100 customers, with a $50/month revenue per customer. That’s a total MRR of $5,000. Two of those customers cancel, resulting in $100 in churned MRR.
However, three other customers upgraded their accounts and are now paying $100/month, resulting in $150 in expansion MRR.
Let’s plug these numbers into our formula:
(100 – 150) / 5000 = -1% revenue churn
Your new MRR is $5,050 without having to acquire new customers.
Want more information? Check out our guide on how to calculate churn.
Tracking Negative Churn
If you’re like me, you probably don’t want to deal with calculations. It's still messy, even if you have a spreadsheet to track it all.
Luckily, there are tools for that. Shameless plug, we have one.
You can track your net revenue churn in Baremetrics and see how it changes over time. You can even see a live demo of the dashboard.
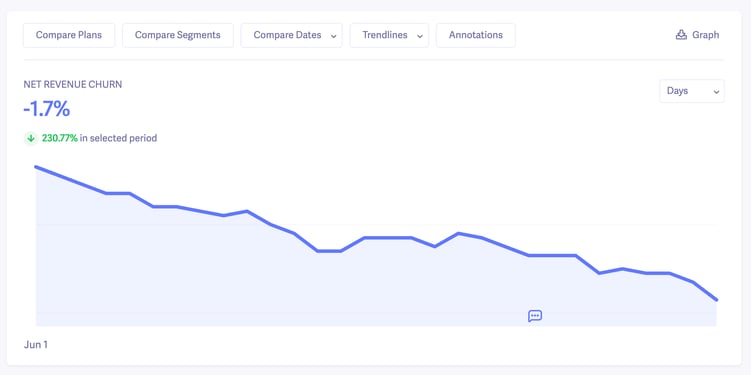
If you want to get really fancy, you can segment your customers and see exactly what’s contributing to your negative churn.
For instance, if we wanted to compare revenue churn for customers who don’t use one of our add-on products, we can add in those segments.
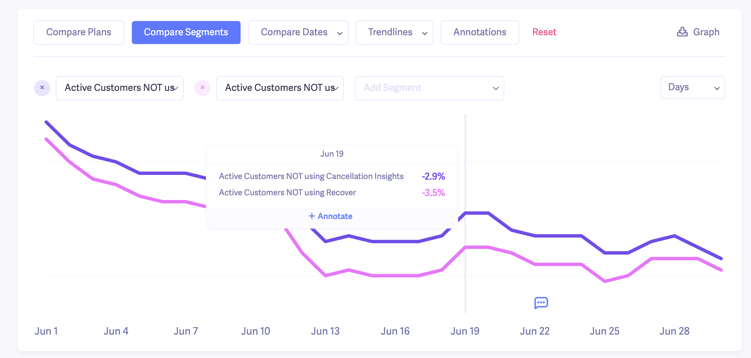
Looking at this data, we can see that if we could get the customers who are not using our add-on products to sign up, we could reduce our net revenue churn even more.
Slicing the data with segments is a great way to do some in-depth churn analysis that can change the trajectory of your business.
If you want to analyze your churn and other metrics, you can see all your data with a free trial!
Achieving Negative Churn
At this stage, you may be wondering, “How can I actually achieve negative net revenue churn?” The formula remains straightforward: focus on two variables—
- Churned MRR
- Expansion MRR
To reach a negative churn rate, your expansion MRR must consistently outpace your churned MRR. In practice, this means implementing strategies to decrease revenue lost while actively increasing the revenue generated from your existing customer base.
Here’s how to do it.
Step 1. Increase MRR from Existing Customers
No matter how low your revenue churn rate is, you’ll never achieve negative churn without increasing your MRR from existing customers.
So, step one needs to be customer expansion.
For most SaaS companies, customer expansion comes from these three strategies:
- Upgrades: Offering a higher-priced version of your product with better features
- Cross-sells: Offering a complementary product
- Add-ons: Offering additional functionality or features to your customer’s current subscription.
Here’s my favorite graphic to illustrate the difference between them.
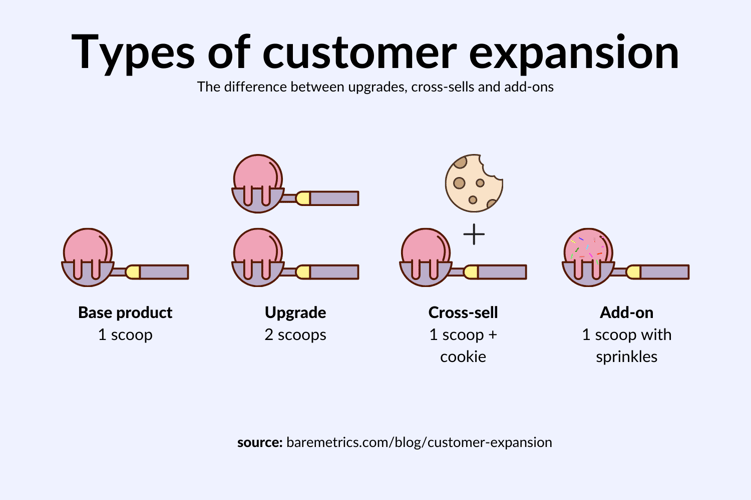
Let’s take a look at examples of how to do all three.
How to Increase MRR With Upgrades
Upgrades are the most common ways to increase expansion MRR. If you have a tiered pricing model, your goal should be to get customers to upgrade their accounts over time.
Depending on your product, this can be difficult or easy.
For instance, look at a product like Later.
They have three pricing tiers.
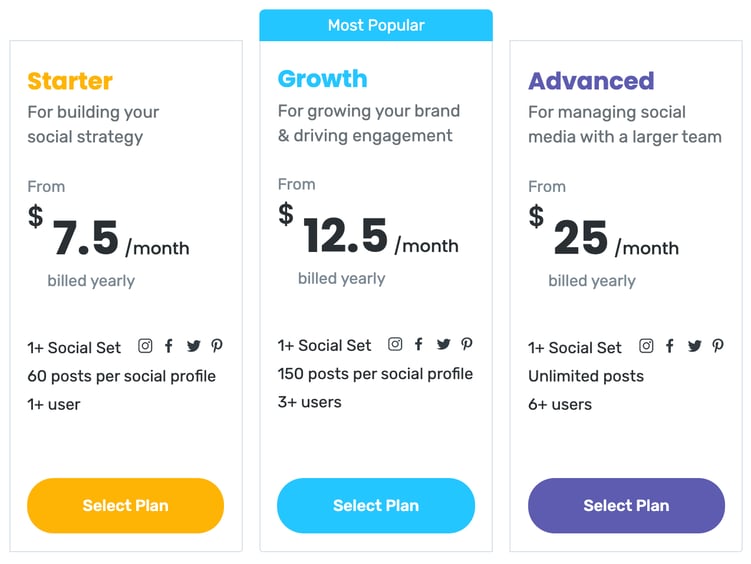
Each tier gives you more posts per social profile and more users. Ideally, as their customers grow their social media accounts, they’ll need to post more and grow their team, so account upgrades are inevitable.
Compare that to Docusign, which also uses tiered pricing. But their prices are based on features.
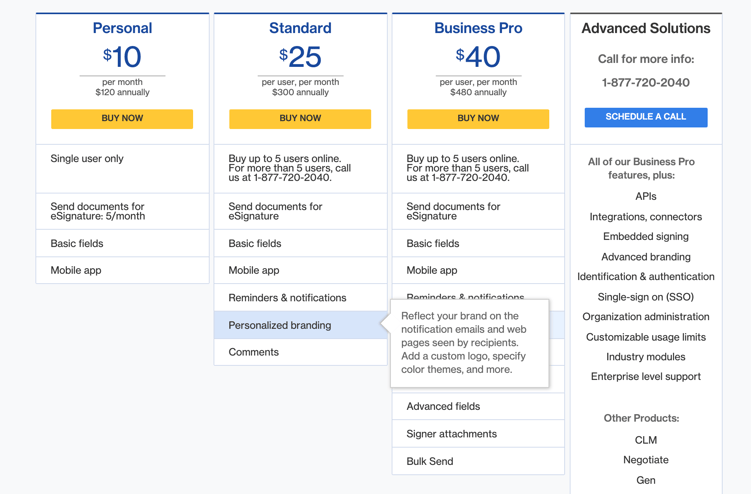
If someone signs up for the Standard account, they’ll only need to upgrade if they want to try new features.
Later’s approach has expansion baked into their pricing model, while Docusign’s customers might need a little more of a “push” to upgrade.
Both approaches work, but Later’s is a little more automated.
How to increase MRR with Cross-Sells
Cross-selling is a good way to increase expansion MRR if you have (or want to make) additional products to complement your flagship one.
Baremetrics, for example, has several products in addition to our core offering, which is a subscription and SaaS analytics platform.
Our Cancellation Insights, for example, will help you discover why customers are canceling, allowing you to make proactive changes before users are at risk for churn.
Baremetrics’ Recover tool is also invaluable, allowing you to spot users who may be at risk for involuntary churn due to canceled or expired credit cards so you can intervene with dunning management.
Both of these can be purchased on their own, but when you combine them with our metrics, they’re insanely more valuable.
For our customers who use our metrics but not our add-ons, we give them the ability to add-on either within their account.
Buffer is another company that started cross-selling a while ago.
For a long time, they had their flagship product, which allows you to schedule social media posts. Now, they have an additional product that allows you to analyze your publishing content.
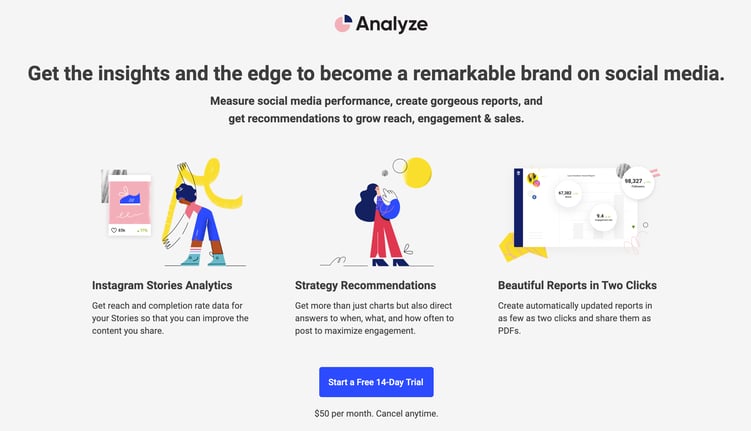
As you can see with both of these examples, cross-selling works with products that are a natural extension of your main SaaS product.
Think of additional subscription products you can offer on top of your main offering that’ll help your customers get even more value. You could even send a survey to your current customers and ask them for ideas.
How to Increase MRR with Add-Ons
Last but not least are add-ons. Unlike cross-selling, add-ons are additional features or extras that build on top of a customer’s current plan.
The best example of this is seat expansion. That’s when a SaaS company charges for additional users, like Ahrefs.
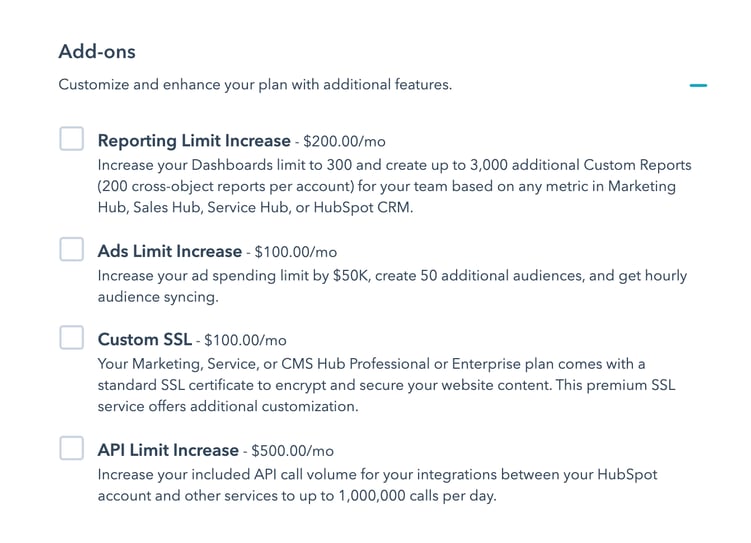
Hubspot is another example. They have a range of add-ons for their marketing suite, that increase your monthly payments.
Be careful with add-ons, though. If you go overboard, you risk coming off as the greedy company trying to nickel and dime customers for every little thing.
Your customers should be able to get value from your base product regardless of whether or not they pay for add-ons.
Keep in mind that all expansions can impact churn rate, which means that calculating LTV can help you better understand your churn metrics.
Step 2: Reduce Churn
The other part of the negative churn puzzle is reducing your revenue churn rate— particularly your revenue churn rate. The less MRR you lose each month, the less additional MRR you need to make up for with customer expansion.
For instance, a company that’s churning $1,000/month needs to get at least that amount in expansion revenue to get close to a net negative churn rate.
Also, don’t fall into the mistake of thinking you can just rely on expansion revenue to fix your churn problem. If you have a 10% churn rate, the chances of you making that up with expansion revenue are slim.
So, how do you reduce revenue churn?
A good place to start is to find out why customers are canceling or downgrading in the first place.
Here’s how we do it at Baremetrics.
Whenever a customer cancels, we send a cancellation survey to find out why.
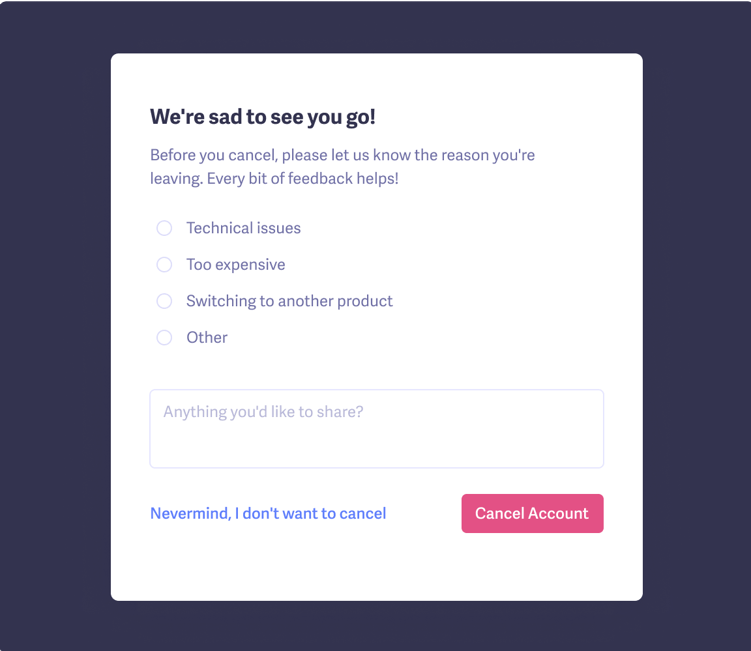
Once they select an answer, we send a follow-up email based on their response.
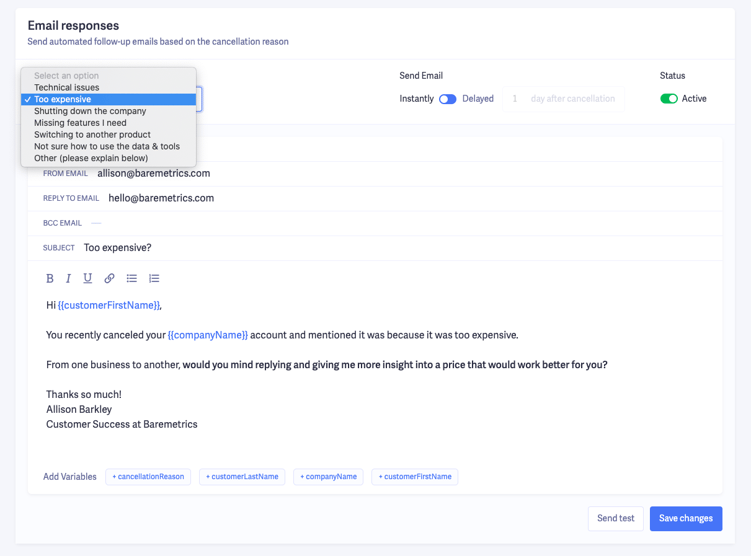
And we collect all the data so we can spot any trends.
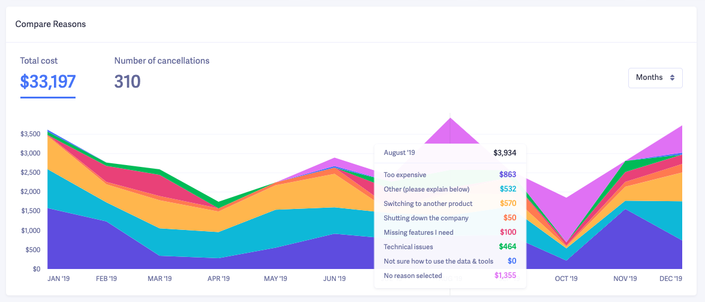
We use our Cancellation Insights add-on to automate the process, making it easy for business owners to see how much recurring revenue they’re losing each month and why.
You can use that data to prioritize what changes to make, starting with the cancellation reasons costing you the most money.
Your SaaS churn rate should decrease over time, which will bring you one step closer to achieving negative churn!
Negative Churn Isn’t “The Norm” - But It's Still Worth Striving For
Negative revenue churn is a powerful achievement, but it’s not a standard outcome for every SaaS company—nor does it happen consistently. At Baremetrics, we’ve experienced months with negative net revenue churn, yet this isn’t the norm each period—and that’s perfectly fine.
Your primary objective should always be to maximize customer retention and expansion, while also strategically acquiring new customers at a sustainable cost. Sustained focus on these areas will drive long-term growth. If you’re able to maintain negative revenue churn in the process, you’ll accelerate that growth even further.
FAQ's
-
What is negative churn in SaaS?
Negative churn happens when the additional revenue from existing customers (through upsells, expansions, or cross-sells) exceeds the revenue lost from customer downgrades or cancellations. In other words, even if you're losing customers, your monthly recurring revenue (MRR) still increases thanks to your current customers spending more over time. -
How do you calculate negative churn?
Negative churn is calculated as:
(Lost MRR – Expansion MRR) ÷ Starting MRR
If the result is a negative percentage, it means you're gaining more revenue from existing customers than you're losing, hence negative churn. -
Why is negative churn important for SaaS companies?
Negative churn indicates strong product-market fit and high customer satisfaction. It allows your business to grow revenue without needing to constantly acquire new customers. Investors view negative churn as a sign of long-term sustainability and efficient monetization. -
What strategies help achieve negative churn?
To achieve negative churn, focus on:
-
Upselling customers to higher-tier plans or add-ons
-
Cross-selling complementary products or features
-
Proactively managing cancellations through feedback loops and intervention
-
Improving onboarding and product engagement to increase retention and expansion potential
-
-
Can a company have negative churn and still lose customers?
Yes. Negative churn refers to revenue, not customer count. You may lose customers, but if the remaining ones spend more (via upgrades or add-ons), your total revenue can still grow month-over-month—resulting in negative churn.
Tired of wasting time on spreadsheets? Get a free trial of Baremetrics today!